Operator in VBA

In Computer Programming An operator is a symbol that can be used to perform specific operations and generate the final result.
There are four type Operator in VBA
- Arithmetic Operators
- String Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
1. Arithmetic Operators in VBA
These are the operators that use at the time of mathematical processes like addition, multiplication, etc.
Below are the arithmetic operators.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Addition |
| – | Subtraction |
| * | Multiplication |
| / | Division |
| Mod | Modulus (it gives Remainder as a result) |
Arithmetic Operators in VBA Video in Hindi
Difference between Division (/) and Modulus (Mod)
- Division operator (/) divides numbers.
- Example
- x = 33;
y = 2;
z = x / y;
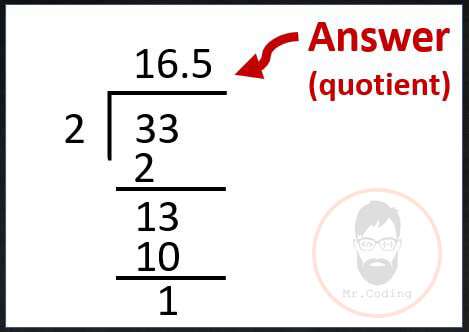
- Modulus operator (%) divides numbers and return remainder as answer.
- Example
- x = 33;
y = 2;
z = x Mod y;
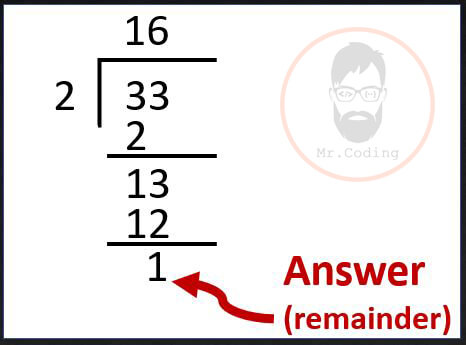
Example of Arithmetic Operator in VBA
Private Sub cmdBttnClick_Click()
Dim num1 As Integer
Dim num2 As Integer
Dim ans As Double
num1 = 33
num2 = 2
ans = num1 + num2
MsgBox ("Addition = " & ans)
ans = num1 - num2
MsgBox ("Subtraction = " & ans)
ans = num1 * num2
MsgBox ("Multiplication = " & ans)
ans = num1 / num2 ' it will gives quotient
MsgBox ("Division = " & ans)
ans = num1 Mod num2 ' it will gives remainder
MsgBox ("Modulus = " & ans)
End Sub
2. String Operators in VBA
In VBA there are mainly two kinds of string operator which are used to joint two different strings into one. String Operator in VBA is as under.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Concatenates two Values if both values are string |
| & | Concatenates two Values |
The above operator joint both two string which is at the left and right side of them. But in case of “+” operator, at least one string value among both sides. If there is the numerical value at both side then “+” operator performs addition operation instead of Concatenation operation.
String Operators in VBA Video in Hindi
Example of Sting Operator or Concatenation in VBA
Private Sub cmdBttnClick_Click()
Dim num1 As Integer
Dim num2 As Integer
Dim name As String
Dim lastName As String
Dim ans1 As String
Dim ans2 As String
Dim ans3 As String
num1 = 5
num2 = 3
ans1 = num1 + num2 ' it will perform addition operation
MsgBox ("Value in ans1 = " & ans1)
name = "Johan"
lastName = "Carter"
ans2 = name + " " + lastName ' it will perform Concatenate operation
MsgBox ("Value in ans2 = " & ans2)
ans3 = name & " " & lastName ' it will perform Concatenate operation
MsgBox ("Value in ans3 = " & ans3)
End Sub
3. Comparison Operators in VBA
When we want to make a decision on the base of comparison of two values at that time, we can use comparison operations. comparison operations are as under.
| Operator | Decription |
|---|---|
| = | Equal |
| <> | Not Equal |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Greater then or equal to |
| <= | Less then or equal to |
Comparison Operators in VBA Video in Hindi
Comparison operators compare two value and return answers in the form of TRUE or FALSE.
Suppose there is two variable X and Y
X= 10 , Y = 10
| Operation | Return Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| X = Y | TRUE | Both values are same |
| X <> Y | FALSE | Both are equal |
| X >= Y | TRUE | X is grater than or equal to Y |
| X <= Y | TRUE | X is less then or equal to Y |
X= 15 , Y = 10
| Operation | Return Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| X > Y | TRUE | X is greater than Y |
| X < Y | FALSE | X is less then Y |
Example of Comparison Operators in VBA
Private Sub cmdBttnClick_Click()
Dim X As Integer
Dim Y As Integer
Dim ans As Boolean
X = 10
Y = 10
ans = (X = Y)
MsgBox ("Operation of X=Y is : " & ans) ' True
ans = (X <> Y)
MsgBox ("Operation of X<>Y is : " & ans) 'False
X = 15
Y = 10
ans = (X > Y)
MsgBox ("Operation of X>Y is : " & ans) ' True
ans = (X < Y)
MsgBox ("Operation of X<Y is : " & ans) 'False
X = 10
Y = 10
ans = (X >= Y)
MsgBox ("Operation of X>=Y is : " & ans) ' True
ans = (X <= Y)
MsgBox ("Operation of X<=Y is : " & ans) ' True
End Sub
In the above example, light gray comments show its output.
4. Logical Operators in VBA
Logical operators will be used when we check more than two variables or to make decisions with more than one condition. Logical operations are as under.
| Operator | Decription |
|---|---|
| AND | Logical AND: Logical AND: it returns TRUE only when all the condition are True |
| OR | Logical OR: it returns TRUE only when at least one condition is True |
| NOT | Logical NOT: It returns Opposite value, if conditions True then it returns FALSE, if the condition is false then it returns TRUE |
Logical Operators in VBA Video in Hindi
Suppose there is three variable X, Y and Z
Value of X=11, Y=18 and Z=25
Now we want to check all the variable are greater than 10 or not
X=11, Y=18 and Z=25
| Operation | Return Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| X>10 AND Y>10 AND Z>10 | TRUE | All value are greater than 10 |
| X<12 OR Y<12 OR Z<12 | TRUE | Any one of variable value is less then 12 |
| NOT (X>10 AND Y>10 AND Z>10) | FALSE | All value are not greater than 10 |
Example of Logical Operator in VBA
Private Sub cmdBttnClick_Click()
Dim X As Integer
Dim Y As Integer
Dim Z As Integer
Dim ans As Boolean
X = 11
Y = 18
Z = 25
ans = (X > 10 And Y > 10 And Z > 10)
MsgBox ("Operation of X>10 And Y>10 And Z>10 is : " & ans) ' True
ans = (X < 12 Or Y < 12 Or Z < 12)
MsgBox ("Operation of X<12 OR Y<12 OR Z<12 is : " & ans) ' True
ans = Not (X > 10 And Y > 10 And Z > 10)
MsgBox ("Operation of Not(X > 10 And Y > 10 And Z > 10) is : " & ans) ' True
End Sub
Leave a Reply